

| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
FORGE-R-OD580*L1520
ETERNAL
Product Description
The working roll used on the roll press of battery equipments is the "core molding component" in the battery electrode manufacturing process. It directly determines the physical properties of the electrode and key indicators such as the energy density and cycle life of the final battery. It is mainly used in the manufacture of mainstream battery electrodes.
Performance Requirement
Hardness: To ensure the precision of battery pole pieces, the surface hardness of the work roll barrel is required to be extremely high. Generally, the surface hardness of the roll barrel is required to be ≥101hsd, and the uniformity of hardness is required to be ≤0.6hsd.
Precision: The machining precision of the work roll is crucial for the uniformity of the pole piece thickness. Typically, it is required that the circular runout be ≤1.0μm and the straightness be ≤2.0μm.
Surface quality: To prevent scratching on the surface of the electrode plate and ensure the rolling effect, the surface of the work roll needs to have a low roughness. At the same time, the positive electrode work roll is often sprayed with WC, while the negative electrode work roll is plated with chromium to improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
Steel Grade
The work roll is generally made of high-hardness alloy steel, such as 9Cr2Mo steel, which has good wear resistance and strength, meeting the requirements of the roll pressing process.
steel grade | Chemical composition /% | |||||||||
C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | Ni | Cu | S | P | |
9Cr2 | 0.80-0.95 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.40 | 1.30-1.70 | — | — | — | — | ≤0.030 | |
8Cr2MoV | 0.80-0.90 | 0.15-0.40 | 0.30-0.50 | 1.80-2.40 | 0.20-0.40 | 0.05-0.15 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.025 | ||
9Cr2Mo | 0.85-0.95 | 0.25-0.45 | 0.20-0.35 | 1.70-2.10 | 0.20-0.40 | — | ||||
9Cr2MoV | 0.20-0.30 | 0.10-0.20 | ||||||||
9Cr3Mo | 2.50-3.50 | 0.20-0.40 | — | |||||||
8Cr3MoV | 0.78-1.10 | 0.40-1.10 | 0.20-0.50 | 2.80-3.20 | 0.20-0.60 | 0.05-0.15 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.025 | |
8Cr5MoV | 0.78-0.90 | 0.40-1.10 | 0.20-0.50 | 4.80-5.50 | 0.20-0.60 | 0.10-0.20 | ≤0.020 | |||
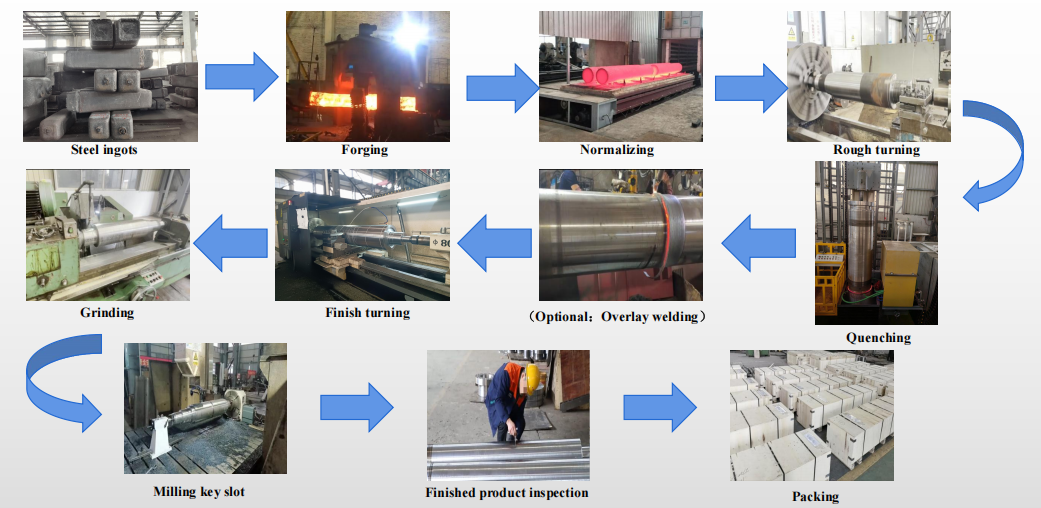
Production Procedure
To ensure the performance of the work roll, a complex manufacturing process is required. For instance, the roll blank is manufactured through specific smelting and forging processes, followed by preliminary heat treatment and final heat treatment to enhance the surface hardness and uniformity of hardness of the roll body.
Forging ,rough machining,heat treatment: normalizing, quenching and tempering,surface quenching ,final processing
Feature

Product Description
The working roll used on the roll press of battery equipments is the "core molding component" in the battery electrode manufacturing process. It directly determines the physical properties of the electrode and key indicators such as the energy density and cycle life of the final battery. It is mainly used in the manufacture of mainstream battery electrodes.
Performance Requirement
Hardness: To ensure the precision of battery pole pieces, the surface hardness of the work roll barrel is required to be extremely high. Generally, the surface hardness of the roll barrel is required to be ≥101hsd, and the uniformity of hardness is required to be ≤0.6hsd.
Precision: The machining precision of the work roll is crucial for the uniformity of the pole piece thickness. Typically, it is required that the circular runout be ≤1.0μm and the straightness be ≤2.0μm.
Surface quality: To prevent scratching on the surface of the electrode plate and ensure the rolling effect, the surface of the work roll needs to have a low roughness. At the same time, the positive electrode work roll is often sprayed with WC, while the negative electrode work roll is plated with chromium to improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
Steel Grade
The work roll is generally made of high-hardness alloy steel, such as 9Cr2Mo steel, which has good wear resistance and strength, meeting the requirements of the roll pressing process.
steel grade | Chemical composition /% | |||||||||
C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | Ni | Cu | S | P | |
9Cr2 | 0.80-0.95 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.40 | 1.30-1.70 | — | — | — | — | ≤0.030 | |
8Cr2MoV | 0.80-0.90 | 0.15-0.40 | 0.30-0.50 | 1.80-2.40 | 0.20-0.40 | 0.05-0.15 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.025 | ||
9Cr2Mo | 0.85-0.95 | 0.25-0.45 | 0.20-0.35 | 1.70-2.10 | 0.20-0.40 | — | ||||
9Cr2MoV | 0.20-0.30 | 0.10-0.20 | ||||||||
9Cr3Mo | 2.50-3.50 | 0.20-0.40 | — | |||||||
8Cr3MoV | 0.78-1.10 | 0.40-1.10 | 0.20-0.50 | 2.80-3.20 | 0.20-0.60 | 0.05-0.15 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.025 | |
8Cr5MoV | 0.78-0.90 | 0.40-1.10 | 0.20-0.50 | 4.80-5.50 | 0.20-0.60 | 0.10-0.20 | ≤0.020 | |||
Production Procedure
To ensure the performance of the work roll, a complex manufacturing process is required. For instance, the roll blank is manufactured through specific smelting and forging processes, followed by preliminary heat treatment and final heat treatment to enhance the surface hardness and uniformity of hardness of the roll body.
Forging ,rough machining,heat treatment: normalizing, quenching and tempering,surface quenching ,final processing

Feature

